Brain
New Hampshire Resident Dies From Rare but Serious Mosquito-Borne Illness
It's one of four cases of Eastern equine encephalitis reported in the U.S. so far this year—and the state's first since 2014
Weight Loss and Diabetes Drug Could Slow Alzheimer's Progression, Preliminary Study Suggests
In a year-long trial, people who received a daily injection of liraglutide showed an 18 percent lower cognitive decline than people who received a placebo
Alzheimer's Blood Test Outperforms Standard Diagnostics in New Study
The blood test accurately diagnosed Alzheimer's around 90 percent of the time, compared to 73 percent for specialists and 61 percent for primary care physicians
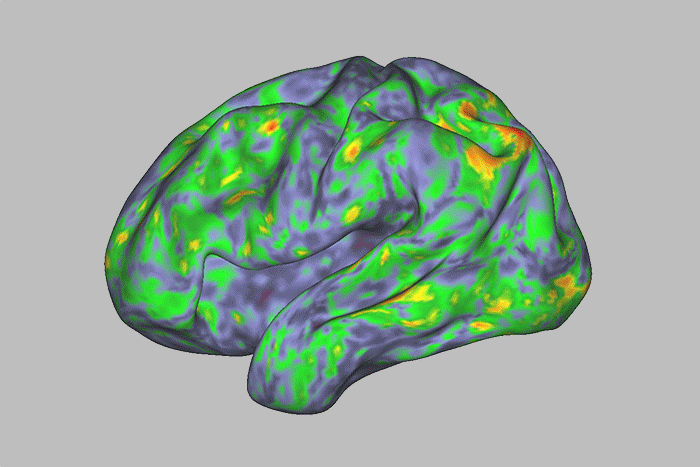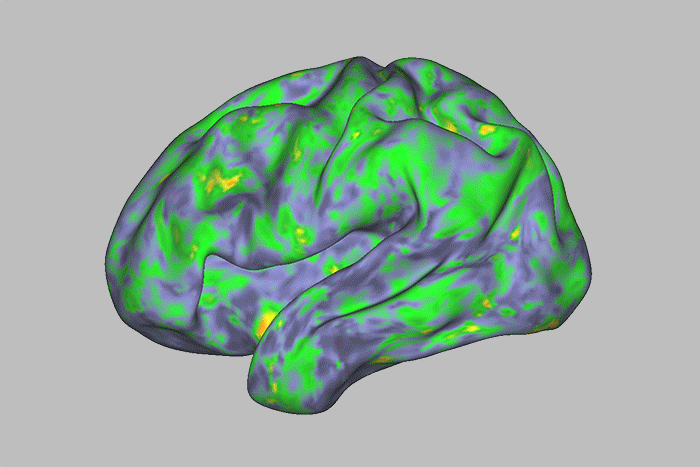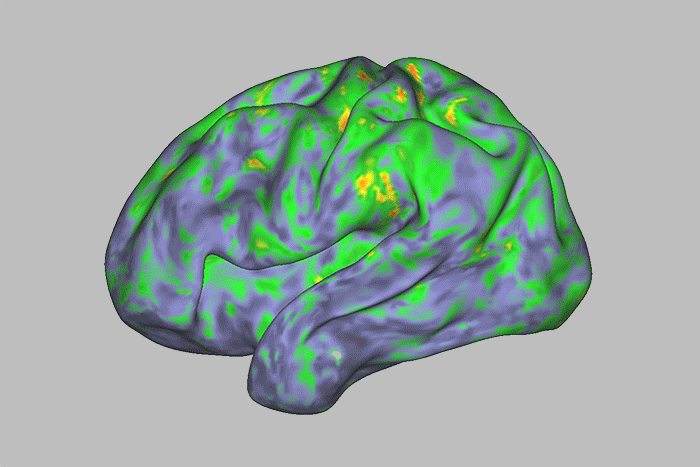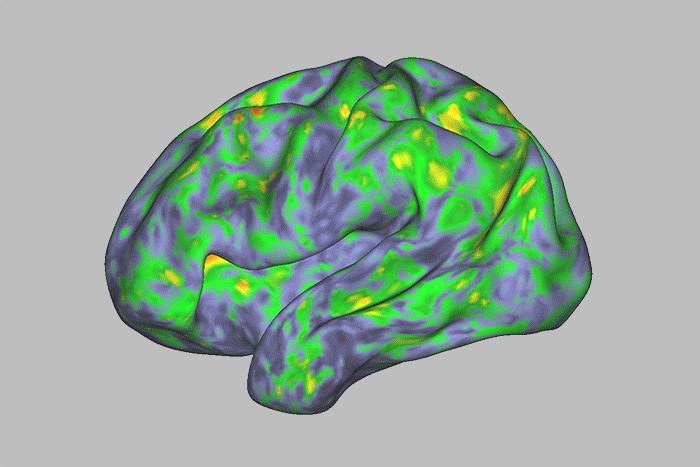
See How the Brain Responds to Psychedelic 'Magic Mushrooms'
A new study mapped large, temporary changes in brain areas related to introspection and one's sense of self, after participants took a dose of the drug psilocybin
How Deep-Sea Comb Jellies Hold Their Shape Under Crushing Pressure
The delicate sea creatures fall apart when brought to the surface but can survive miles deep in the ocean due to special cell wall structures, according to a new study
New Blood Test for Predicting Parkinson's Disease With A.I. Shows Promise, Study Suggests
In preliminary research, scientists identified eight protein anomalies in the blood of patients with Parkinson's, which they say can help diagnose the disease up to seven years before symptoms appear
Can Technology Help Us More Accurately Diagnose Mental Illnesses?
A new wave of tools promises to offer quicker, more objective assessments to help patients and clinicians
How Do We Know When to Pee?
The basic urge is surprisingly complex and can go awry as we age
After Brain Injuries, Doctors and Families Should Take More Time With Life Support Decisions, Research Finds
A small study suggests some severe traumatic brain injury patients can later recover a level of independence or return to their pre-injury lives
Scientists Imaged and Mapped a Tiny Piece of Human Brain. Here's What They Found
With the help of an artificial intelligence algorithm, the researchers produced 1.4 million gigabytes of data from a cubic millimeter of brain tissue
A Modified Psychedelic Toad Toxin Reduces Signs of Depression and Anxiety in Mice, Study Suggests
Colorado River toads produce a psychoactive toxin that some have claimed has medical benefits. The new research suggests these benefits could be achieved without hallucinations
Are Days Passing Too Quickly? Memorable Experiences Might Help Dilate Your Sense of Time, Research Suggests
How we process time is linked to things we see, according to a new study, which found memorable, non-cluttered imagery can make moments seem to last longer
Almost All People With Two Copies of This Genetic Variant Develop Signs of Alzheimer's Disease, Study Finds
The research focused on a variant called APOE4 and largely looked at people of European ancestry—risk levels are different for other groups, the authors say
Researchers Breed Mice With Hybrid Brains Containing Cells From Rats
In one experiment, rat neurons helped mice restore their senses of smell—the first time any animal has perceived the world through the sensory hardware of another species
How Intelligent Was T. Rex? Scientists Suggest the Dinosaurs Were Like 'Smart, Giant Crocodiles'
A new paper refutes the idea that T. rex was as brainy as a baboon, furthering the debate on the extinct reptile's intellect
Why Do Some People Always Get Lost?
Research suggests that experience may matter more than innate ability when it comes to a sense of direction
Why Are Some People Left-Handed? Scientists Identify Rare Genetic Variants That May Be Linked to the Trait
The variants are present in fewer than 1 percent of people, but they were 2.7 times more likely to appear in lefties than in righties
Why Do We Want to Squish and Squeeze Things That Are Cute? Science Has the Answer
The response dubbed “cute aggression” by researchers is the brain’s attempt to self-regulate when confronted with intense emotion
Bad Sleep Can Make You Feel Years Older Than You Really Are, Study Suggests
After just two nights of short sleep, a person’s “subjective age,” or how old they feel, can spike by more than four years
From the JogBra to Gatorade to Breakaway Basketball Rims, Sports Are a Field for Invention
A new exhibition at the National Museum of American History aims to inspire the next generation of innovators
Page 1 of 21
:focal(3140x2093:3141x2094)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/93/88/9388ea77-b284-47e4-97b6-83cfa256e72a/gettyimages-1927045430.jpg)
:focal(2500x1667:2501x1668)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/8a/d6/8ad64075-57a2-4239-93d4-6baf3489bedd/gettyimages-1793641166.jpg)
:focal(1061x707:1062x708)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/24/2f/242f7b45-9432-4e4d-9deb-1beb7c4845a9/gettyimages-1443155227.jpg)
:focal(1060x713:1061x714)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/78/11/7811e0eb-8364-458a-a9b4-14a582663169/gettyimages-90050101.jpg)
:focal(1061x707:1062x708)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/71/67/71670cf2-6c5d-41c2-a41b-1ba60b600e07/gettyimages-1348149832.jpg)
:focal(800x602:801x603)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/e1/05/e105d9e9-0802-4b1e-b2a5-8f1cafb247c9/mentalhealthtec-v2_web.jpg)
:focal(800x602:801x603)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/18/66/186616cb-4800-471a-b199-f546735811a3/gettyimages-643755291_web.jpg)
:focal(1060x706:1061x707)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/fb/71/fb714e35-ec75-4a66-add9-11a062954706/gettyimages-619266666.jpg)
:focal(1664x1093:1665x1094)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/c7/ba/c7baacef-cb16-4351-bd03-27bd56c1b461/connectomics2024-1-excitatoryneuronsoriginal.png)
:focal(2557x1705:2558x1706)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/0d/25/0d256629-a9c7-4fa0-8c34-88192c102901/16643564344_90ca76c136_o.jpg)
:focal(1500x943:1501x944)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/d8/73/d873f475-0061-4cf6-a677-a74c62e328e3/50368695116_85e24b80b8_o.jpg)
:focal(1815x1210:1816x1211)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/e7/0a/e70a08dc-1ec3-4c16-8f62-bccfa20435da/gettyimages-151036433.jpg)
:focal(2808x1872:2809x1873)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/3f/9a/3f9a09b9-6c57-4354-827f-6f45f25bb0dd/gettyimages-1234160574.jpg)
:focal(1024x683:1025x684)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/54/b1/54b11c8a-cce4-43fd-83b9-41ce0bd64ec8/juvenile_t_rex_at_carnegie_museum_of_natural_history_2013-12-14.jpg)
:focal(800x602:801x603)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/07/20/0720406e-51f0-4bee-b91a-34b050bf3886/navigation-3200x1200_web.jpg)
:focal(1060x712:1061x713)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/ea/27/ea2773f4-7b02-48f5-af92-052f8753d2ba/gettyimages-532640376.jpg)
:focal(2538x1692:2539x1693)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/e3/e4/e3e47e00-5d89-4f7f-94b2-866086e00f8d/b76kgy.jpg)
:focal(1060x706:1061x707)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/ab/86/ab86b9fe-90cf-4e15-b6ae-cc6b10ddd883/gettyimages-1464159268.jpg)
:focal(1000x695:1001x696)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/bd/c8/bdc8b8ed-f664-4be0-a886-b1bf177d047b/jn2024-00176.jpg)